Types of Functions
The following table list the formula and key properties of the most
of the functions discussed in this text:
These formulas are often refer to as Mathematical Models:
| Mathematical
Models: The use of a function to represent a mathematical problem whether
real or theoretical |
Table 1.4 Types of Functions by Formula(s)
and Properties: a, b, k, m, s, r, A, B,
C, D are constants
| Directly Proportional Models
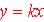 ,
k is a constant ,
k is a constant
1 point can define function |
Inverse Related Models
 ,
graphs have Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes ,
graphs have Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes
1 point can define function |
Absolute Value Models
 actually 2 functions:
actually 2 functions:

Domain Specific Linear Fcts. |
| Linear Models
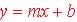
Rate, m is a constant value
2 points to define function
The y-int at b |
Exponential Models
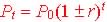 or
or
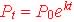 or
or 
The rate is in % (related to r)
2 points defines function |
Exponential Money Models

 ,
r is yearly rate ,
r is yearly rate
 ,
y-int at ,
y-int at 

|
| Logarithm Models
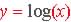
Logs are the inverse of Exponential
No value for function 
If 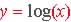 then
then
 its inverse
its inverse
|
Piecewise Models
Different functions for specified values (domains) for independent variable,
x |
Quadratic Models:
Vertex Form: 
Zero Form:
Standard Form: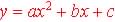
A polynomial with at most 2 zeros |
| Periodic Models:

Cyclic fcts that repeats at constant intervals - periods
Easily formulated from graph |
Trigonometric Models:
Law of Sines
Law of Cosines
Properties of Right Triangles
Numerous Identities |
Transformation of Functions:
Given 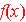 Transform
Transform

|
| Inverse of Functions:
Given:
Find:  |
Polynomials:


|
Rational Models:
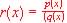 p(x) & q(x) are polynomials (Asymptotes)
p(x) & q(x) are polynomials (Asymptotes)
|
Click here for graphs
of functions: |