
College Algebra
by Example Series

Chapter
1.1. Equations
|
College Algebra by Example Series |
Is x = b? (true or false?), x is called a variable and can assume any value.
3 Possible Outcomes:
1. Identity: Every possible values of x is true
For example, sin2 x + cos2 x = 1, this is true for all real values of x.
Many solutions so many roots.
2. Impossible equations or solutions (Contradictions) - no solution:
For example, x = x + 2, no real number is a solution.
Also 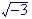
No solution so no root.
3. Conditional solutions or equations:
For example, 3x + 1 = 7, only one or few values of x satisfies the equation,
here x = 2.
One or few solutions or root(s).
Summary of Types of Equations:
| Identity | Conditional | No Solution |
| Property:
Both sides of the equations are the same |
One or more solutions when solving for the variable |
No real solutions exist |
| Key Examples
1. 3(x + 3) = 3x + 9 2. 23 = 8 3. x2 + 5x + 6 =(x + 3)(x + 2) |
Examples: 2x + 1 > 0, any value of x > -½ (x + 1)(x - 3) = 0, x = -1 ans 3 |
1. 2. |